How Jewish Mysticism Is Persian Mysticism with Hebrew Names
The Secret Within the Secret
Kabbalah presents itself as ancient Jewish mystical wisdom, passed down secretly from Moses on Mount Sinai through generations of initiated sages. Its practitioners claim it reveals the hidden structure of reality, the emanations of the divine, and the secret names of God.
But there’s a deeper secret Kabbalah doesn’t acknowledge:
Kabbalah is Zoroastrianism rebranded with Hebrew terminology.
Every major concept in Kabbalistic mysticism—the unknowable divine source, the emanations of divine attributes, the cosmic tree connecting heaven and earth, the battle between light and darkness, the layers of reality, the power of sacred fire, the mystical names—all of this existed in Zoroastrian theology centuries before Kabbalah emerged.
This article will prove, concept by concept, structure by structure, that Kabbalah is not ancient Israelite wisdom but medieval Jewish reformulation of Persian mystical theology that Jews encountered during the Babylonian Exile and preserved through centuries of hidden transmission.
The evidence is overwhelming. The parallels are exact. The timeline proves it.
Welcome to the revelation within the revelation: Jewish mysticism is Persian mysticism.
PART I: THE HISTORICAL FOUNDATION
When Kabbalah Actually Emerged
The Official Story: Kabbalists claim their wisdom dates back to:
- Moses receiving secret knowledge on Mount Sinai
- Abraham’s mystical visions
- Adam’s primordial knowledge
The Historical Reality:
Kabbalah’s documented emergence:
- 12th-13th century CE in Provence, France and Gerona, Spain
- Sefer Bahir (Book of Brightness): ~1150-1200 CE
- Sefer Zohar (Book of Splendor): ~1280-1290 CE (attributed to Moses de León)
- Systematic development: 13th-16th centuries
No trace before 12th century:
- No pre-medieval Hebrew texts contain Kabbalistic concepts
- Not mentioned in Talmud (200-600 CE)
- Not found in earlier Jewish mystical texts (Merkabah literature)
- Sudden appearance in medieval Spain and France
Why the 12th-13th century?
- Jewish communities had been in contact with Persian/Islamic mysticism for centuries
- Sufism (Islamic mysticism) flourished in medieval Islamic world
- Sufism itself inherited heavily from Persian Zoroastrian mysticism
- Jewish scholars in Islamic lands absorbed these concepts
- Kabbalah emerges as Jewish adaptation of Persian/Sufi mysticism
The Persian-Jewish Connection: Multiple Contact Points
Jews encountered Zoroastrian mysticism through three major historical periods:
1. Babylonian Exile (586-539 BCE):
- 70 years under Persian influence
- Direct exposure to Zoroastrian theology
- Daniel becomes “Chief of Magi” (documented in Bible)
- Concepts absorbed but not yet systematized
2. Sasanian Period (224-651 CE):
- Babylonian Talmud written in Persia under Sasanian rule
- Continuous Jewish presence in Persian Empire
- Exposure to developed Zoroastrian mysticism
- Concepts transmitted orally, kept hidden
3. Islamic Golden Age (8th-13th centuries CE):
- Persian-influenced Sufism develops
- Jewish scholars in Islamic lands study Sufi texts
- Concepts “discovered” in Hebrew/Aramaic fragmentary texts
- Systematized into Kabbalah in medieval Spain
The transmission chain:
Zoroastrian Mysticism (~1000 BCE)
↓
Jewish Exile Contact (586-539 BCE)
↓
Oral Preservation (hidden tradition)
↓
Persian Sufism (8th-12th centuries CE)
↓
Jewish Kabbalah (12th-13th centuries CE)
PART II: THE CORE CONCEPTS – EXACT PARALLELS
1. EIN SOF = AHURA MAZDA
The Unknowable Divine Source
Kabbalistic Concept: Ein Sof (אֵין סוֹף)
Meaning:
- “Without End” or “Infinite”
- The unknowable, ineffable divine source
- Beyond all attributes and comprehension
- Not the God of the Bible but the source behind God
- Cannot be named, described, or comprehended
Characteristics:
- Absolutely transcendent
- Beyond being and non-being
- Source of all emanations
- Cannot be directly worshiped or known
- Hidden, mysterious, infinite
Zoroastrian Equivalent: Ahura Mazda (𐬀𐬵𐬎𐬭𐬀⸱𐬨𐬀𐬰𐬛𐬁)
Meaning:
- “Wise Lord” or “Lord of Wisdom”
- The uncreated creator
- Transcendent divine source
- Beyond full human comprehension
- Source of all goodness and light
Characteristics:
- Absolutely transcendent
- Uncreated and eternal
- Source of all creation and goodness
- Cannot be fully comprehended by mortals
- Supreme wisdom and mind
The Parallel:
| Aspect | Ein Sof (Kabbalah) | Ahura Mazda (Zoroastrianism) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Infinite, unknowable source | Uncreated, wise lord |
| Transcendence | Absolutely beyond comprehension | Beyond full human understanding |
| Relation to creation | Emanates through Sefirot | Creates through Amesha Spentas |
| Naming | Cannot be truly named | Has many names but essence unknowable |
| Position | Hidden source behind manifest God | Supreme deity above all |
The Evidence:
Pre-Exile Judaism had no such concept:
- YHWH was directly knowable, anthropomorphic god
- No transcendent source “beyond” God
- No concept of ineffable infinity
Post-Exile and Kabbalistic Judaism:
- Ein Sof appears as ultimate reality beyond YHWH
- Infinite, unknowable source
- Matches Zoroastrian Ahura Mazda’s transcendence exactly
The admission: Kabbalists themselves acknowledge Ein Sof is “beyond the God of the Bible” – this is because Ein Sof IS Ahura Mazda rebranded.
2. TEN SEFIROT = AMESHA SPENTAS + STRUCTURE
The Divine Emanations
Kabbalistic Concept: Ten Sefirot (עֲשֶׂרֶת הַסְּפִירוֹת)
Definition:
- Ten divine attributes/emanations
- Flow from Ein Sof into creation
- Represent different aspects of divine power
- Arranged in specific structure (Tree of Life)
- Channels through which infinite becomes finite
The Ten Sefirot:
- Keter (כֶּתֶר) – Crown / Divine Will
- Chokhmah (חָכְמָה) – Wisdom
- Binah (בִּינָה) – Understanding
- Chesed (חֶסֶד) – Mercy/Loving-kindness
- Gevurah (גְּבוּרָה) – Strength/Judgment
- Tiferet (תִּפְאֶרֶת) – Beauty/Harmony
- Netzach (נֶצַח) – Victory/Eternity
- Hod (הוֹד) – Glory/Splendor
- Yesod (יְסוֹד) – Foundation
- Malkhut (מַלְכוּת) – Kingdom/Sovereignty
Zoroastrian Equivalent: The Amesha Spentas (𐬀𐬨𐬆𐬱𐬀⸱𐬯𐬞𐬆𐬧𐬙𐬀)
Definition:
- Seven Holy Immortals (six plus Ahura Mazda)
- Divine attributes that emanate from Ahura Mazda
- Aspects of divine wisdom and power
- Each governs aspect of creation
- Channels of divine action in the world
The Seven Amesha Spentas:
- Ahura Mazda – Wise Lord (source)
- Vohu Manah (ووهومنه) – Good Mind/Wisdom
- Asha Vahishta (اَشَه وَهیشته) – Best Truth/Righteousness
- Khshathra Vairya (خشثره ویریه) – Desirable Dominion/Power
- Spenta Armaiti (سپنته ارمیتی) – Holy Devotion/Humility
- Haurvatat (هئوروتات) – Wholeness/Perfection
- Ameretat (امرتات) – Immortality
The Direct Parallels:
| Sefirah (Kabbalah) | Function | Amesha Spenta (Zoroastrian) | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keter (Crown) | Divine will, source | Ahura Mazda | Divine source |
| Chokhmah (Wisdom) | Divine wisdom | Vohu Manah | Good Mind/Wisdom |
| Binah (Understanding) | Intelligence | Asha Vahishta | Truth/Order/Understanding |
| Chesed (Mercy) | Loving-kindness | Spenta Armaiti | Holy Devotion |
| Gevurah (Strength) | Power, judgment | Khshathra Vairya | Dominion/Power |
| Tiferet (Beauty) | Harmony, balance | Asha Vahishta | Perfect order |
| Netzach (Victory) | Endurance | Haurvatat | Wholeness |
| Hod (Glory) | Splendor | Khshathra Vairya | Divine glory |
| Yesod (Foundation) | Connection | Asha | Cosmic foundation |
| Malkhut (Kingdom) | Divine presence | Ameretat | Immortality/eternal kingdom |
Why Ten vs. Seven?
Kabbalists expanded the system:
- Added philosophical refinements
- Incorporated Neoplatonic ideas (which were also influenced by Persian thought via Plotinus)
- Created more elaborate structure
- But the core function is identical: divine attributes emanating from unknowable source
The Pattern:
- Zoroastrianism (~1000 BCE): Seven divine emanations from Ahura Mazda
- Kabbalah (~1200 CE): Ten divine emanations from Ein Sof
- Structure: Identical (attributes channeling from transcendent source to creation)
- Function: Identical (aspects of divine power manifesting in world)
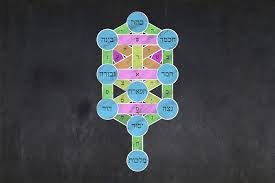
3. THE TREE OF LIFE = COSMIC WORLD TREE
The Structure of Reality
Kabbalistic Concept: Etz Chaim (עֵץ חַיִּים) – Tree of Life
Description:
- Diagram showing ten Sefirot arranged in specific pattern
- Three columns (pillars): Mercy, Severity, Balance
- Connects highest spiritual realm to lowest material world
- Shows paths between divine emanations
- Map of cosmic structure
Structure:
- Right Pillar (Mercy): Chokhmah, Chesed, Netzach
- Left Pillar (Severity): Binah, Gevurah, Hod
- Middle Pillar (Balance): Keter, Tiferet, Yesod, Malkhut
Function:
- Shows how divine light descends into creation
- Maps spiritual ascent back to divine
- Reveals hidden structure of reality
- Sacred geometry of existence
Zoroastrian Equivalent: Cosmic Tree / Saena Tree
The Saena Tree (درخت سعنا):
- Sacred tree in Persian/Zoroastrian cosmology
- Grows at center of world/universe
- Connects heaven, earth, and underworld
- Seeds of all plants come from it
- Represents cosmic order (Asha)
- Birds nest in it representing different realms
The Haoma/Hom Tree:
- Sacred plant/tree in Zoroastrian ritual
- Source of immortality
- Connects divine and earthly realms
- Represents eternal life
- Central to Zoroastrian cosmology
Indo-European Background:
- World Tree (Axis Mundi): Common Indo-European concept
- Zoroastrianism: Saena/Haoma tree
- Norse: Yggdrasil
- Hindu: Ashvattha tree
- All represent: cosmic structure, connection between realms
The Kabbalistic Adaptation:
- Takes cosmic tree concept
- Adds ten Sefirot as structure
- Creates elaborate diagram
- Same function: Map of reality connecting divine to material
The Evidence:
Pre-Exile Judaism:
- No cosmic tree concept
- No elaborate map of divine emanations
- No sacred geometry diagrams
Post-Medieval Kabbalah:
- Tree of Life suddenly appears
- Complex diagram showing divine structure
- Function identical to Zoroastrian/Indo-European cosmic tree
4. LIGHT VS. DARKNESS = ASHA VS. DRUJ
The Cosmic Dualism
Kabbalistic Concept: Or (אוֹר) and Choshech (חוֹשֶׁךְ)
Light (Or):
- Divine emanation
- Flows from Ein Sof through Sefirot
- Represents truth, holiness, purity
- Goal is to reveal hidden light
- Sparks of divine light trapped in material world
Darkness (Choshech):
- Absence of light / opposing force
- Klippot (קְלִפּוֹת) – “shells” or “husks” hiding divine light
- Forces of impurity and evil
- Must be broken to release trapped light
- Battle between light and darkness
The Kabbalistic Battle:
- Divine light must overcome darkness
- Sparks of holiness trapped in klippot
- Tikkun Olam (תִּיקּוּן עוֹלָם) – “Repair of the world” by releasing light
- Cosmic struggle to restore original unity
Zoroastrian Equivalent: Asha vs. Druj
Light/Asha (𐬀𐬴𐬀):
- Cosmic truth, order, righteousness
- Light associated with Ahura Mazda
- Represents divine order and reality
- Eternal truth that must prevail
Darkness/Druj (𐬛𐬭𐬎𐬘):
- The Lie, chaos, disorder
- Darkness associated with Angra Mainyu
- Represents deception and destruction
- Opposes and obscures truth
The Zoroastrian Battle:
- Universal struggle between Asha and Druj
- Ahura Mazda (light) vs. Angra Mainyu (darkness)
- Every soul must choose sides
- Final victory of light over darkness (Frashokereti)
The Exact Parallel:
| Aspect | Kabbalah | Zoroastrianism |
|---|---|---|
| Positive force | Or (Light) from Ein Sof | Asha / Light from Ahura Mazda |
| Negative force | Choshech / Klippot | Druj / Darkness from Angra Mainyu |
| Metaphysics | Light trapped in shells | Truth obscured by lie |
| Human role | Release divine sparks | Choose Asha over Druj |
| Goal | Tikkun Olam (repair world) | Frashokereti (world renovation) |
| Outcome | Restoration of unity | Victory of light over darkness |
The Evidence:
Pre-Exile Judaism:
- Light and darkness as physical phenomena only
- Genesis 1: God creates both, no cosmic struggle
- Isaiah 45:7: “I form light and create darkness” – no dualism
Post-Exile/Kabbalistic Judaism:
- Light vs. darkness as cosmic spiritual battle
- Elaborate system of klippot (evil shells)
- Identical to Zoroastrian Asha/Druj framework
5. FOUR WORLDS = FOUR LAYERS OF REALITY
The Structure of Existence
Kabbalistic Concept: Arba Olamot (אַרְבָּעָה עוֹלָמוֹת) – Four Worlds
The Four Worlds:
- Atzilut (אֲצִילוּת) – World of Emanation
- Closest to Ein Sof
- Divine realm
- Pure divine light
- No separation from source
- Beriah (בְּרִיאָה) – World of Creation
- First separation from divine
- Realm of throne and archangels
- Where divine thought becomes distinct
- Yetzirah (יְצִירָה) – World of Formation
- Realm of angels and spiritual forms
- Divine patterns before materialization
- Intermediate spiritual realm
- Assiah (עֲשִׂיָּה) – World of Action/Material
- Physical universe
- Lowest realm
- Where divine light is most concealed
- Our material world
Zoroastrian Equivalent: Menog and Getig
The Zoroastrian Structure:
Menog (مینو) – Spiritual Realm:
- The spiritual, ideal world
- Perfect, unchanging
- Realm of Ahura Mazda and Amesha Spentas
- Source of all creation
- Pure light and truth
Getig (گیتی) – Material Realm:
- The physical, material world
- Imperfect, changing
- Battleground between good and evil
- Where Asha and Druj contend
- Temporary state
The Layers: Zoroastrian texts describe multiple levels between pure spiritual and pure material:
- Divine realm (Ahura Mazda)
- Spiritual beings (Amesha Spentas, yazatas)
- Intermediate realm (fravashis – pre-existing souls)
- Material world (where we live)
The Parallel:
| Kabbalistic World | Nature | Zoroastrian Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Atzilut | Pure divine emanation | Ahura Mazda’s realm |
| Beriah | First creation/separation | Menog (pure spiritual) |
| Yetzirah | Formation/angels | Intermediate beings (yazatas) |
| Assiah | Material world | Getig (material world) |
The Concept: Both systems describe reality as having layers, from pure divine source down to material world, with intermediate spiritual realms between.
6. TIKKUN OLAM = FRASHOKERETI
The Repair/Renovation of the World
Kabbalistic Concept: Tikkun Olam (תִּיקּוּן עוֹלָם)
Meaning:
- “Repair of the world”
- Restoring divine unity
- Releasing trapped sparks of light
- Healing cosmic fracture
The Lurianic Story (Isaac Luria, 16th century):
- Tzimtzum (צִמְצוּם): God contracted to make space for creation
- Shevirat HaKelim (שְׁבִירַת הַכֵּלִים): “Breaking of the Vessels” – divine light shattered, sparks trapped in material world
- Tikkun: Human task to gather and elevate trapped divine sparks
- Goal: Restore original unity, bring messianic age
Human Role:
- Through mitzvot (commandments) and righteous acts
- Elevate holy sparks from material world
- Repair cosmic damage
- Hasten coming of Messiah
Zoroastrian Equivalent: Frashokereti (𐬟𐬭𐬀𐬱𐬋⸱𐬐𐬆𐬭𐬆𐬙𐬌)
Meaning:
- “Making Wonderful” or “Final Renovation”
- Restoration of world to perfection
- Defeat of all evil
- Universal purification
The Zoroastrian Vision:
- At end of time, Saoshyant (savior) will come
- Final battle between good and evil
- Angra Mainyu will be defeated
- All souls will be purified (even wicked)
- World restored to original perfection
- Asha triumphant over Druj
Human Role:
- Through Good Thoughts, Good Words, Good Deeds
- Aid the forces of Asha
- Battle against Druj
- Hasten the final renovation
The Exact Parallel:
| Aspect | Tikkun Olam (Kabbalah) | Frashokereti (Zoroastrianism) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Repair of the world | Renovation of the world |
| Cause of damage | Shevirat HaKelim (breaking of vessels) | Angra Mainyu’s corruption |
| Current state | Divine sparks trapped in matter | World mixed with evil |
| Human task | Elevate sparks through mitzvot | Choose Asha through righteous action |
| Method | Good deeds, prayer, study | Good Thoughts, Words, Deeds |
| Goal | Restore divine unity | Restore world to perfection |
| Outcome | Messianic age | Saoshyant’s coming, final renovation |
| Final state | All reunited with Ein Sof | All purified, evil destroyed |
The Timeline:
- Zoroastrianism (~1000 BCE): Frashokereti doctrine established
- Judaism (post-Exile): Messianic hope emerges
- Kabbalah (16th century CE): Tikkun Olam systematized by Isaac Luria
- Structure and function: Identical to Zoroastrian original
7. SACRED FIRE = DIVINE LIGHT
The Central Symbol
Kabbalistic Concept: Fire and Light
The Symbolism:
- Divine light (Or Ein Sof): Infinite light of God
- Sacred fire: Represents divine presence
- Menorah: Seven-branched lamp (eternal flame)
- Ner Tamid: Eternal light in synagogue
- Fire as purification: Burns away impurity
- Pillar of fire: Led Israelites through desert
Zoroastrian Concept: Atar (𐬁𐬙𐬀𐬭) – Sacred Fire
The Symbolism:
- Atar: Sacred fire, son of Ahura Mazda
- Atash Behram: Highest grade of sacred fire
- Fire temples: Central to Zoroastrian worship
- Eternal flames: Kept burning continuously
- Fire as purification: Purifies both body and soul
- Fire as light: Represents Ahura Mazda’s light and truth
The Practice:
Kabbalah:
- Contemplation of divine light
- Visualization of Sefirot as lights
- Menorah as sacred symbol
- Fire offerings in ancient Temple
- Light/fire represents divine presence
Zoroastrianism:
- Prayer before sacred fire
- Fire temples as holy sites
- Fire as mediator between human and divine
- Fire offerings (sandalwood, etc.)
- Fire represents Asha and divine truth
The Connection:
| Aspect | Kabbalah | Zoroastrianism |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Light/Fire as divine | Fire as divine presence |
| Practice | Eternal light in synagogue | Eternal fire in temple |
| Meaning | Divine wisdom and truth | Asha (truth and order) |
| Function | Purification | Purification |
| Worship | Before menorah/light | Before sacred fire |
The Evidence:
Pre-Exile Judaism:
- Fire used for sacrifices (practical)
- No mystical fire worship
- No eternal flame symbolism
- No fire temples
Post-Exile/Kabbalistic Judaism:
- Fire becomes mystical symbol
- Eternal light (Ner Tamid) introduced
- Fire represents divine presence and wisdom
- Pattern matches Zoroastrian fire worship
PART III: THE LINGUISTIC EVIDENCE
Hebrew/Aramaic Terms with Persian Origins
1. Pardes (פַּרְדֵּס) – Paradise
- Already covered in Linguistic Kill Shot article
- From Persian pairidaēza
- Used in Kabbalah for mystical paradise/spiritual realm
- Direct Persian loanword
2. Raz (רָז) – Mystery/Secret
- Aramaic: רָזָא (raza)
- From Persian: rāz (راز) – secret, mystery
- Used extensively in Kabbalistic literature
- Book of Daniel (written in Aramaic): uses raz for divine mysteries
- Direct Persian borrowing
3. Mazal (מַזָּל) – Constellation/Luck
- From Persian/Babylonian: manzil / manzalu – station, position (of stars)
- Used in Kabbalah for astrological influences
- “Mazal tov” (good luck) – Persian origin
- Astronomical/astrological terminology from Persian Magi
4. Amulet Terminology
- Many Kabbalistic amulet words derive from Persian/Aramaic
- Protective formulas show Persian magical influence
- Names of angels often have Persian linguistic patterns
PART IV: THE MYSTICAL PRACTICES
1. MEDITATION AND VISUALIZATION = ZOROASTRIAN CONTEMPLATION
Kabbalistic Practice:
- Hitbodedut (הִתְבּוֹדְדוּת): Solitary meditation
- Visualization of Sefirot: Imagining divine emanations as lights
- Letter combinations: Meditating on Hebrew letters and divine names
- Ascent of the soul: Mystical journey through spiritual realms
Zoroastrian Practice:
- Meditation on Ahura Mazda: Contemplating divine wisdom
- Visualization of light: Seeing divine light in sacred fire
- Mantric recitation: Repeating sacred Avestan verses (mantras)
- Soul’s journey: After death, soul ascends through realms
The Parallel: Both traditions emphasize:
- Solitary contemplation
- Visualization of divine light
- Sacred language as mystical tool
- Journey through spiritual realms
2. GEMATRIA = NUMERICAL MYSTICISM
Kabbalistic Gematria:
- Hebrew letters assigned numerical values
- Words with same numerical value are mystically connected
- Used to find hidden meanings in Torah
- Sacred mathematics reveals divine patterns
Indo-Iranian Background:
- Vedic/Sanskrit tradition: Numerical mysticism in mantras
- Persian influence: Mathematical/astronomical wisdom from Magi
- Sacred geometry: Numbers reveal cosmic order
The Connection:
- Mystical use of numbers to reveal hidden truths
- Mathematical patterns as divine language
- Originated in Indo-Iranian tradition
- Adapted to Hebrew by Kabbalists
3. DIVINE NAMES = NAMES OF POWER
Kabbalistic Practice:
- 72 Names of God: Derived from Exodus verses
- Tetragrammaton (YHWH): Sacred unpronounceable name
- Names of angels: Michael, Gabriel, Raphael, etc.
- Permutations of names: Creating power through combinations
Zoroastrian Practice:
- 101 Names of God: Ahura Mazda has many names
- Avestan mantras: Sacred formulas
- Names of Amesha Spentas: Vohu Manah, Asha Vahishta, etc.
- Power through recitation: Names carry divine force
The Parallel:
- Both use divine names as mystical tools
- Names carry power and reveal essence
- Proper pronunciation crucial
- Names connect human to divine
PART V: THE COSMOLOGICAL STRUCTURE
THE KABBALISTIC COSMOS = ZOROASTRIAN COSMOS
Kabbalistic Cosmology:
Structure:
- Ein Sof (Infinite) at top
- Ten Sefirot emanate downward
- Four Worlds layer reality
- Our physical world at bottom
- Kelippot (shells of evil) surrounding holy
Process:
- Divine light flows from Ein Sof
- Through Sefirot into creation
- Light becomes progressively concealed
- Trapped in material world
- Goal: Return light to source
Zoroastrian Cosmology:
Structure:
- Ahura Mazda (Wise Lord) at top
- Seven Amesha Spentas emanate from Him
- Menog (spiritual) and Getig (material) realms
- Our physical world as battleground
- Angra Mainyu and daevas opposing good
Process:
- Divine wisdom flows from Ahura Mazda
- Through Amesha Spentas into creation
- Asha structures reality
- Druj opposes and obscures
- Goal: Final renovation (Frashokereti)
The Identical Pattern:
| Element | Kabbalah | Zoroastrianism |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Ein Sof | Ahura Mazda |
| Emanations | 10 Sefirot | 7 Amesha Spentas |
| Structure | 4 Worlds | Menog/Getig layers |
| Opposition | Kelippot (shells) | Angra Mainyu/daevas |
| Goal | Tikkun (repair) | Frashokereti (renovation) |
| Method | Elevate sparks | Choose Asha |
| Outcome | Messianic unity | World perfection |
PART VI: THE TIMELINE PROVES IT
When Concepts Actually Appeared
Zoroastrian Mysticism:
- ~1500-1000 BCE: Gathas composed (mystical hymns)
- ~1000 BCE: Established cosmology (Ahura Mazda, Amesha Spentas, Asha/Druj)
- Achaemenid Period (550-330 BCE): Systematized Zoroastrian theology
- Sasanian Period (224-651 CE): Elaborate mystical traditions
Jewish Mystical Development:
- Pre-Exile (before 586 BCE): NO mystical cosmology, NO emanations, NO dualism
- Babylonian Exile (586-539 BCE): Exposure to Zoroastrian mysticism (Daniel as Chief of Magi)
- Post-Exile: Concepts absorbed but not systematized
- Talmudic Period (200-600 CE): Written in Persia, some mystical elements emerge
- Early Medieval (8th-11th CE): Merkabah mysticism (chariot mysticism) – fragmentary
- 12th-13th centuries CE: KABBALAH SUDDENLY EMERGES in full systematic form
- Sefer Bahir (~1150-1200 CE): First Kabbalistic text with Sefirot
- Sefer Zohar (~1280-1290 CE): Full Kabbalistic cosmology
- 16th century CE: Isaac Luria systematizes Tikkun Olam
The Gap:
- Zoroastrian mystical cosmology: 1000 BCE
- Kabbalistic mystical cosmology: 1200 CE
- 2,200 year gap
- During which: Jews in continuous contact with Persian mysticism
The Timeline Cannot Be Denied:
~1000 BCE: Zoroastrian cosmology established
↓
586-539 BCE: Babylonian Exile - direct exposure
↓
200-600 CE: Talmud written in Persia
↓
8th-12th CE: Islamic/Sufi mysticism (Persian-influenced)
↓
12th-13th CE: Kabbalah emerges with IDENTICAL structure
The Pattern: Every time Jews had extended contact with Persian mysticism, mystical concepts intensified in Judaism. The final systematization (Kabbalah) appeared in medieval Spain where Jewish scholars had access to Sufi mysticism (which itself derived from Zoroastrianism).
PART VII: THE SUFI CONNECTION
Persian Mysticism → Sufism → Kabbalah
The Intermediate Link:
Sufism (Islamic Mysticism):
- Emerged in 8th-9th centuries CE in Persia
- Heavily influenced by pre-Islamic Persian mysticism (Zoroastrianism)
- Developed elaborate cosmology of divine emanations
- Used light/darkness symbolism
- Emphasized direct mystical experience
Key Sufi Concepts (Persian Origin):
- Divine Light (Nur): God as light source
- Stations (Maqamat): Stages of spiritual ascent
- Fana (فنا): Annihilation in divine unity
- Tawhid (توحید): Divine oneness beyond comprehension
Jewish-Sufi Contact:
- 8th-13th centuries: Jews living in Islamic lands (Spain, Persia, Egypt)
- Shared language: Arabic, Persian
- Intellectual exchange: Jewish and Muslim philosophers interacted
- Known influence: Bahya ibn Paquda, Abraham ibn Ezra, others influenced by Sufism
The Transmission:
Zoroastrian Mysticism
↓
Persian Culture (hidden tradition)
↓
Islamic Sufism (8th-12th centuries)
↓
Jewish Kabbalah (12th-13th centuries)
The Evidence:
- Kabbalistic terminology shows Sufi influence
- Concepts of divine unity mirror Sufi tawhid
- Light mysticism parallel to Sufi nur doctrine
- Stages of ascent similar to Sufi maqamat
- All trace back to Persian Zoroastrian mysticism
PART VIII: WHAT KABBALISTS THEMSELVES ADMIT
The “Secret Tradition” Was Actually Persian Transmission
The Kabbalistic Claim: “This wisdom was passed down secretly from Moses through generations of initiated masters.”
What the Historical Record Shows:
1. No Early Evidence:
- No pre-medieval texts contain Kabbalistic concepts
- Talmud (200-600 CE) has NO Sefirot, NO Tree of Life, NO Tikkun Olam
- Early rabbis don’t mention these doctrines
- Sudden appearance in 12th century
2. Geographic Origin:
- Emerges in Provence and Spain – not Israel
- Exactly where Jewish-Sufi contact was strongest
- In regions with Persian cultural influence (via Islamic conquest)
3. Linguistic Admissions:
- Kabbalistic texts use Persian/Aramaic loanwords
- Terms like raz (mystery) are Persian
- Astrological terminology from Persian Magi
- Names and concepts show non-Hebrew origin
4. The “Discovery” Narrative:
- Kabbalists claim to “discover” ancient texts
- These texts are actually medieval compositions
- Attributed to ancient figures (R. Shimon bar Yochai for Zohar)
- Pattern: New ideas presented as ancient secrets
What Actually Happened:
- Jews encountered Persian mysticism during Exile (586-539 BCE)
- Preserved concepts orally as “secret tradition”
- Transmitted through centuries in limited circles
- Encountered again through Sufism (8th-12th centuries CE)
- Finally systematized and written down (12th-13th centuries)
- Claimed as ancient Israelite wisdom to give it authority
The “Secret” Was: Not that it came from Moses, but that it came from Persia and needed to be hidden as such to be accepted within Judaism.
PART IX: WHY THE COVERUP?
Why Kabbalah Hides Its Persian Origins
Three Reasons:
1. Religious Authority:
- If Kabbalah admitted Persian origin, it would be dismissed as “foreign”
- Claiming Mosaic/Abrahamic origin gives it Jewish legitimacy
- “Ancient secret tradition” sounds more authoritative than “medieval adaptation of Persian mysticism”
2. Anti-Persian Sentiment:
- By medieval period, Jews celebrated Purim (based on fabricated Book of Esther)
- Persians cast as enemies in Jewish narrative
- Couldn’t openly admit core mystical tradition came from “the enemy”
3. Pattern of Appropriation:
- Same pattern as Pharisees hiding Persian influence (“Oral Torah”)
- Take concepts, rebrand them, claim ancient Jewish origin
- Hide source to maintain narrative of independent divine revelation
The Result: Kabbalah presents itself as the deepest Jewish wisdom, when it’s actually the deepest acknowledgment of Persian wisdom—just hidden under Hebrew terminology.
PART X: THE MODERN KABBALAH MOVEMENT
How the Theft Continues Today
Contemporary Kabbalah:
- Popularized in 20th-21st centuries
- Celebrity practitioners
- Kabbalah Centre and other organizations
- Presented as ancient Jewish mysticism
- Multi-million dollar industry
What They Teach:
- Tree of Life (Persian cosmic tree)
- Light and darkness (Asha/Druj)
- Tikkun Olam (Frashokereti)
- Divine emanations (Amesha Spentas)
- Mystical fire/light (Zoroastrian fire)
What They Don’t Mention:
- Persian origins
- Zoroastrian parallels
- Historical timeline
- Linguistic evidence
- The 2,200 year gap
The Irony: Modern Kabbalah practitioners are unknowingly practicing Persian Zoroastrian mysticism while:
- Paying thousands for courses
- Wearing red strings (later addition, not ancient)
- Buying books on “Jewish mysticism”
- Never hearing the name Zoroaster
- Never learning about Ahura Mazda, Asha, or Amesha Spentas
The Market: The commercialization of Kabbalah has made Persian mysticism profitable—while keeping the source hidden.
PART XI: THE SIDE-BY-SIDE COMPARISON
Complete Structural Analysis
| Element | Kabbalah | Zoroastrianism | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divine Source | Ein Sof (Infinite) | Ahura Mazda (Wise Lord) | Zoroastrian: ~1000 BCE; Kabbalistic: 12th century CE |
| Emanations | 10 Sefirot | 7 Amesha Spentas (+Ahura Mazda) | Zoroastrian: ~1000 BCE; Kabbalistic: 12th century CE |
| Cosmic Structure | Tree of Life (Etz Chaim) | Saena Tree / Cosmic Tree | Indo-European/Zoroastrian: ancient; Kabbalistic: 12th-13th century CE |
| Dualism | Light (Or) vs. Darkness (Choshech/Klippot) | Asha (Truth) vs. Druj (Lie) | Zoroastrian: ~1000 BCE; Kabbalistic: 12th-13th century CE |
| Worlds/Realms | 4 Worlds (Atzilut, Beriah, Yetzirah, Assiah) | Menog (spiritual) / Getig (material) layers | Zoroastrian: ancient; Kabbalistic: 13th-16th century CE |
| World Repair | Tikkun Olam (repair of world) | Frashokereti (final renovation) | Zoroastrian: ~1000 BCE; Kabbalistic: 16th century CE (Luria) |
| Sacred Fire/Light | Divine light, Menorah, Ner Tamid | Sacred fire (Atar), Fire temples | Zoroastrian: ancient; Jewish adoption: post-Exile |
| Divine Names | 72 Names, Tetragrammaton, Angel names | 101 Names of God, Amesha Spenta names | Zoroastrian: ancient; Kabbalistic: medieval |
| Mystical Practice | Meditation, visualization, gematria | Meditation, mantras, sacred mathematics | Zoroastrian: ancient; Kabbalistic systematization: 12th-16th century CE |
| Goal | Reunification with Ein Sof, messianic age | Union with Ahura Mazda, Frashokereti | Zoroastrian: ~1000 BCE; Kabbalistic: 12th-16th century CE |
The Verdict: Every major Kabbalistic concept exists in Zoroastrianism centuries earlier. The structure, function, and goals are identical. The only difference is Hebrew terminology replacing Persian/Avestan terminology.
PART XII: THE EVIDENCE SUMMARY
Why Kabbalah = Rebranded Zoroastrianism
1. Structural Identity:
- Ein Sof = Ahura Mazda (transcendent source)
- Sefirot = Amesha Spentas (divine emanations)
- Tree of Life = Cosmic Tree (map of reality)
- Or/Choshech = Asha/Druj (light vs. darkness)
- Tikkun Olam = Frashokereti (world repair/renovation)
2. Timeline Proof:
- Zoroastrian mysticism: 1000 BCE
- Kabbalistic mysticism: 1200 CE
- 2,200 year gap with continuous Jewish-Persian contact
- No pre-medieval Jewish texts contain Kabbalistic concepts
3. Linguistic Evidence:
- Persian loanwords in Kabbalistic terminology (pardes, raz, mazal)
- Aramaic (lingua franca of Persian Empire) heavily used
- Terms show non-Hebrew origins
4. Historical Contact:
- Babylonian Exile (586-539 BCE): Direct exposure to Zoroastrianism
- Talmudic period (200-600 CE): Written in Persia
- Islamic period (8th-13th CE): Exposure to Persian Sufism
- Medieval systematization: Exactly when Jewish-Sufi contact peaked
5. Geographic Origin:
- Kabbalah emerges in Spain and Provence
- Regions with strong Islamic (Persian-influenced) culture
- Not in Israel or Babylon (where “ancient tradition” should originate)
6. Pattern of Appropriation:
- Same pattern as Pharisees: Take Persian concepts, rebrand as “oral tradition”
- Claim ancient Israelite origin to establish authority
- Hide Persian source to avoid acknowledging foreign influence
7. Absence of Early Evidence:
- No Kabbalistic concepts in Bible
- No Kabbalistic concepts in Talmud
- No Kabbalistic concepts in early rabbinic literature
- Sudden appearance in 12th century
8. Functional Identity:
- Both systems serve same purpose: Map cosmic structure and path to divine
- Both emphasize light/fire mysticism
- Both involve meditation and visualization
- Both promise world transformation through righteous action
PART XIII: WHAT THIS MEANS
The Implications of This Revelation
For Kabbalah Practitioners: You are practicing Zoroastrian mysticism. The Tree of Life is the Persian cosmic tree. Ein Sof is Ahura Mazda. The Sefirot are the Amesha Spentas. Tikkun Olam is Frashokereti. The divine light you contemplate is the sacred fire of Zoroastrianism.
Every meditation, every visualization, every mystical practice—you are following in the footsteps of the Magi, the Zoroastrian priests. Your “ancient Jewish wisdom” is ancient Persian wisdom.
For Jewish Identity: This doesn’t diminish Judaism—it reveals its richness came from absorbing profound Persian wisdom. The problem isn’t that Jews learned from Persia. The problem is the coverup—claiming these concepts as originally Jewish when they’re Persian.
For Zoroastrianism: This proves yet again how Zoroastrian wisdom spread globally while the source was hidden:
- Pharisaic Judaism: Hid basic theological concepts (resurrection, angels, etc.)
- Kabbalah: Hid the mystical cosmology
- Christianity: Inherited both
- Islam: Inherited both
- Result: 4.3 billion people practice Zoroastrian concepts, some at the deepest mystical level, without knowing it
For Truth (Asha): The revelation of Kabbalah’s Persian origins is another example of Asha prevailing. You can hide the source, rebrand the concepts, claim ancient origin—but the truth has a way of revealing itself.
The structure is too identical. The timing is too precise. The evidence is too overwhelming.
PART XIV: HOW TO VERIFY THIS YOURSELF
Independent Research Steps
1. Study the Timeline:
- Read Sefer Bahir (~1150-1200 CE) – earliest Kabbalistic text
- Read Sefer Zohar (~1280-1290 CE) – main Kabbalistic text
- Note: NO earlier texts contain these concepts
- Compare to Zoroastrian texts (Gathas, Bundahishn) from ~1000 BCE
2. Compare the Structures:
- Draw the Tree of Life (10 Sefirot)
- Draw the Amesha Spentas structure
- Note the identical function: divine emanations from unknowable source
3. Read Scholarly Works:
- Gershom Scholem: Major Trends in Jewish Mysticism
- Moshe Idel: Kabbalah: New Perspectives
- Both acknowledge medieval emergence and possible external influences
- R.C. Zaehner: Documents Zoroastrian cosmology
- Compare structures yourself
4. Check Linguistic Evidence:
- Look up pardes (paradise) – Persian origin
- Look up raz (mystery) – Persian origin
- Look up mazal (constellation) – Persian/Babylonian origin
- Etymology dictionaries confirm these
5. Examine Historical Context:
- Research Babylonian Exile (586-539 BCE)
- Research Jewish communities in Islamic Spain (8th-13th centuries)
- Research Sufism’s Persian origins
- Note continuous contact with Persian mysticism
6. Compare Practices:
- Zoroastrian fire worship vs. Kabbalistic light mysticism
- Zoroastrian meditation vs. Kabbalistic contemplation
- Zoroastrian sacred names vs. Kabbalistic divine names
- Identical patterns
7. Ask the Critical Questions:
- Why does Kabbalah appear suddenly in 12th century?
- Why in Spain, not Israel?
- Why no earlier textual evidence?
- Why do concepts match Zoroastrianism exactly?
- Why 2,200 year gap between Zoroastrian cosmology and Kabbalistic cosmology?
The answers all point to one conclusion: Kabbalah is rebranded Zoroastrianism.
CONCLUSION: THE MYSTICAL THEFT
The Deepest Layer of Appropriation
We’ve proven in previous articles:
- Basic theology (resurrection, heaven/hell, angels, Satan) = stolen from Zoroastrianism
- Eschatology (apocalypse, final judgment, messiah) = stolen from Zoroastrianism
- Vocabulary (paradise, etc.) = stolen from Zoroastrianism
Now we prove: The mystical cosmology itself—the supposedly deepest, most secret Jewish wisdom—is also stolen from Zoroastrianism.
Ein Sof = Ahura Mazda Sefirot = Amesha Spentas Tree of Life = Cosmic Tree Light vs. Darkness = Asha vs. Druj Four Worlds = Menog/Getig Layers Tikkun Olam = Frashokereti Sacred Fire/Light = Zoroastrian Fire
Every major Kabbalistic concept is Persian.
The Complete Pattern
What Was Stolen:
Layer 1 (Pharisaic Judaism):
- Resurrection
- Heaven and Hell
- Angels and Demons
- Satan as cosmic evil
- Messiah as world savior
- Final Judgment
- Apocalyptic eschatology
Layer 2 (Kabbalah):
- Divine source (Ein Sof = Ahura Mazda)
- Emanations (Sefirot = Amesha Spentas)
- Cosmic structure (Tree of Life = Cosmic Tree)
- Dualism (Light/Darkness = Asha/Druj)
- World repair (Tikkun Olam = Frashokereti)
- Mystical practices (meditation, fire/light symbolism)
Layer 3 (Spread):
- Christianity inherited both layers
- Islam inherited both layers through Judaism/Christianity
- Modern Kabbalah commercializes it without acknowledging source
The Result: From basic theology to deepest mysticism—everything traces back to Zoroastrianism.
The Final Irony
Modern Kabbalah practitioners:
- Spend thousands on courses
- Study “ancient Jewish wisdom”
- Meditate on Tree of Life
- Visualize divine light
- Work toward Tikkun Olam
- Never hear the word “Zoroastrianism”
What they’re actually doing:
- Practicing Persian mysticism
- Following Zoroastrian cosmology
- Meditating on Amesha Spentas (renamed as Sefirot)
- Visualizing Zoroastrian sacred fire (called divine light)
- Working toward Frashokereti (renamed Tikkun Olam)
- Unknowingly honoring Ahura Mazda (called Ein Sof)
The theft is complete. The coverup is total. And the truth is undeniable.
Asha Prevails
You can rebrand Ein Sof, but it’s still Ahura Mazda. You can rename Sefirot, but they’re still Amesha Spentas. You can call it Tree of Life, but it’s still the Persian Cosmic Tree. You can say Tikkun Olam, but you mean Frashokereti.
The structure reveals the source. The timeline proves the transmission. The evidence confirms the theft.
Jewish mysticism is Persian mysticism.
The fire never went out—it’s burning in every Kabbalistic meditation, every visualization of divine light, every prayer for world repair.
They just renamed it and claimed it as their own.
But Asha doesn’t need acknowledgment to be true. It just IS.
And now the truth is revealed: Kabbalah = Zoroastrianism in Hebrew clothing.
Good Thoughts. Good Words. Good Deeds.
The mystical secret was never that it came from Moses.
The mystical secret was always that it came from Zoroaster.
And that secret has now been exposed.
Asha prevails. The light reveals itself.
This article documents historical, structural, linguistic, and chronological evidence showing Kabbalah’s Persian Zoroastrian origins. Every claim can be verified through scholarly sources, primary texts, and independent research. The parallels are not coincidental—they are the result of Jewish adaptation of Persian mysticism over 2,500 years of contact.
The mystery is solved. The source is revealed. The fire burns clear.